SEO tips are a dime a dozen. We've cherry-picked the quickest and easiest to help get your website working and your traffic growing.
The busiest SEO pros can be forgiven for overlooking some of the quickest, easiest fixes when optimising their website for search.
And if you're not quite pro-level yet, or SEO isn't your speciality, it's easy to miss one or more of the many updates to SEO best practices that seem to roll out on a weekly basis. (Google sure likes to keep us all on our toes.)
With six in every 10 marketers saying that improving SEO and growing their organic presence is their top inbound marketing priority, we've put together this article of 12 SEO tips and tricks to help you achieve exactly that — as quickly and easily as possible.
Some of these improvements can be made in minutes. Others are slightly more technical, so in each case, we'll outline the fastest and most simple way of cracking on with them yourself.
Actioning any of these fundamental SEO exercises will lay great foundations for improving your rankings and increasing your organic traffic. Implement all of them well and you're guaranteed to pip your competitors to the top of the search engine results pages.
Let's go:
1. Fix your broken links

Fixing broken links is a great example of a quick SEO win.
At a time when user experience and on-page engagement are second to none, a broken link is going to cause frustration and put off the very people you're trying the hardest to reach.
It's not only your visitors whose impression of you and your website will suffer. Google doesn’t like you irritating your visitors either, meaning broken links are a huge no-no in the search engine's eyes. If your broken links go unnoticed or uncared for, they can build up, leading to 'link rot' and ultimately damaging your website’s organic ranking and traffic.
What to do if you discover broken links:
Where one broken link exists, others tend to follow. If you've found a broken link somewhere on your site, the first step you should take is to scan the rest of the site for others. Use a tool such as SEMrush or the online brokenlinkchecker tool to achieve this in no time.
With your list of broken links in a spreadsheet, the next step is to remove or fix them. Broken links can occur for a number of reasons:
- You've entered an incorrect URL when linking to the destination page
- The linked destination (whether one of your pages or a page on an external site) no longer exists, causing what's known as a 404 error
- The destination website itself has permanently moved or no longer exists
- You've linked to a page or site that's behind a firewall prohibiting outside access (such as an Intranet site or a restricted access area on a website)
If the broken link is outbound, it's a quick and simple task to replace it with a healthy, functioning one. Make sure any outbound links go to respectable websites with a solid domain authority and content that will genuinely help your readers.
"If an internal link (to another of your pages) has broken, and it's not because of a typo in the URL, your best bet is to set a redirect in place," says Dan Stillgoe, one of our inbound consultants.
"A broken link can happen for all sorts of reasons but chiefly it will be because the destination page's URL has changed (or the page has been taken down altogether)." Dan Stillgoe, Inbound Consultant, BabelQuest
'A redirect will make sure that when someone next visits that URL, they will automatically be sent to a different URL, answering their question or query seamlessly, without interrupting their visit or stopping them in their tracks', he adds.
Related read: 6 key benefits of performing an SEO audit
2. Create unique title tags
 As the SEO specialists at Moz describe it, "A title tag is an HTML element that specifies the title of a web page. Title tags are displayed on search engine results pages (SERPs) as the clickable headline for a given result, and are important for usability, SEO, and social sharing. The title tag of a web page is meant to be an accurate and concise description of a page's content."
As the SEO specialists at Moz describe it, "A title tag is an HTML element that specifies the title of a web page. Title tags are displayed on search engine results pages (SERPs) as the clickable headline for a given result, and are important for usability, SEO, and social sharing. The title tag of a web page is meant to be an accurate and concise description of a page's content."
'A title tag (alongside your meta description) is your opportunity to convince your next customer to click through to your website from the search results', reveals Gem Latimer, one of our HubSpot platform consultants and former inbound strategist.
"Looking at title tags through an SEO lens, if Google can see that lots of searchers are clicking on your entries, it will favour them when someone next searches for that term. ('Everyone's interested in what you have to say, so it must be good, right?')"
"Improving your title tags isn't difficult and you can prioritise the pages that need it most, so it doesn't have to take long, either." Gem Latimer, HubSpot Platform Consultant, BabelQuest
How to write standout title tags:
The big takeaways from this description are accurate and concise. The title needs to accurately communicate to the reader what the page behind the search result talks about, explains, or offers. It's a promise to the reader that if they click on that result, this is what they will find.
Of course, a title tag is also restricted by space. This is where concise comes in; Google typically displays the first 50–60 characters of a title tag, so you are best placed to write within this limit. If you must write a longer title, make sure the most important or engaging elements are near the start.
Other helpful title tag tips (if you want to spend a little longer):
- Including your page's primary keyword in the title, so it jumps out at people searching for that exact term
- Reviewing your competition in the SERPS to make sure your title stands out from the crowd
- Working any awesome offers or other tempting descriptors into the title to really encourage a click through
- If location is important to your business, working this into the title tag can catch the eye of people in your target area
- Noticed a particular phrase or wording that's improving click-throughs? Try it on several other pages and start experimenting to see what works best
3. Create unique meta descriptions
 A simple yet effective SEO tip for any business looking to improve its organic performance and attract more visitors to its site is to improve the strength of its meta descriptions.
A simple yet effective SEO tip for any business looking to improve its organic performance and attract more visitors to its site is to improve the strength of its meta descriptions.
A meta description is a snippet of between 150-160 characters that summarises a page’s content. When Google displays your page in the search results, it's this snippet of copy that it shows to the searcher.
The primary purpose of a meta description is to encourage the searcher to click on your result.
Treat that snippet as free advertising copy that has one purpose: to get the searcher to choose your entry above any other.
To transform the effectiveness of your meta descriptions:
Again, using tools such as SEMrush or Screaming Frog, ascertain whether all of your pages have meta descriptions. Fill in the blanks for pages that don't have them and edit any duplicate meta descriptions across the site so that they’re all unique.
"Ensure to include the focus keyword for which you’ve optimised the page. This isn't a key ranking factor but it will help to make your meta description more engaging to people searching for that term," reveals Gem.
"You should also be able to add meta descriptions to your blog category and tag pages, providing even more clues to search engines as to your areas of expertise." Gem Latimer, HubSpot Platform Consultant, BabelQuest
Gem's final takeaway? 'Remember to include a call-to-action in your meta description! Use active words to invite users to click on your link, phrases such as “find out more here” and “take a look now”.'
4. Search optimise your images with alt text
 As the old saying goes, 'a picture says a thousand words', unless that picture is online and the thing reading it is Google or another search engine.
As the old saying goes, 'a picture says a thousand words', unless that picture is online and the thing reading it is Google or another search engine.
In this case, Google and other search engines are actually blind to what that image is. They depend on something called alt text — short descriptions you can add to each image — to understand what that image is showing and when to return it in a search result.
Whether you're a large enterprise with an extensive blog or a small business writing and publishing content for the first time, remembering to add alt text to your website images is a quick win when it comes to optimising those pages for search.
Don't get me wrong — alt text isn't a huge ranking signal, but in today's competitive digital space, every little helps.
Alt text for images: best practices
Alice Crick, one of our content writers, says: "To make sure Google is showing your images for the relevant image searches, it's important that your alt text accurately describes those images."
"Think of alt text as a description to tell search engines what the image is of — it's effectively ‘image SEO'." Alice Crick, Copywriter, BabelQuest
Using trusty SEMrush or ScreamingFrog (other popular SEO tools are available), figure out which of the images across your website currently have alt text. "For those that don't, a quick SEO win is to go in and add a brief description. As best practice (and to show Google that your image is really relevant to your target keyword), incorporate the page's primary keyword into one of the images on that page," says Alice.
"You shouldn't spam your target keyword into every image's alt text, so I recommend that you use a few keyword variations. Check out tools such as LSIgraph to find alternatives for your target keyword."
More image alt text best practices include the following:
- Be specific when describing the image. Consider what the image is as well as what context you're using it in.
- Limit your alt text description to fewer than 125 characters. Anything beyond this is too long for what should essentially be short, accurate, keyword-optimised description of an image.
- Get straight to the point. The primary function of alt text is to describe an image to Google and other search engines, so there's no need to write 'An image of...' or 'This picture is showing...'. Google already knows it's looking at an image.
5. Review the indexing status of your site
 Indexing is the process of adding web pages into Google search. If one of your pages isn’t indexed, it’s impossible to drive any organic traffic to it as it won’t show up in Google’s SERPs.
Indexing is the process of adding web pages into Google search. If one of your pages isn’t indexed, it’s impossible to drive any organic traffic to it as it won’t show up in Google’s SERPs.
Now imagine if your whole website was no-indexed (we've seen stranger things). Suddenly, that lack of organic traffic and dramatic drop in site traffic starts to make more sense...
"No-indexing can happen for many different reasons," says our inbound consultant Dan Stillgoe. "The biggest one we see is human error. A check of the indexing status of your site doesn't take long and it's just there to make sure there aren't any no-indexed pages flying under the radar."
How to check if your web pages are no-indexed
- Go to Google and type 'site:yourdomain.com'
- 'The result will show how many of your pages Google has indexed', reveals Dan. 'Is this a different result than you had anticipated?'
- Too few pages suggest that Google is struggling to index all of your pages, whereas a higher amount of pages indicates an issue with duplicate content.'
- If there are any discrepancies, you want to go into (or set up!) your Google Search Console account (formerly webmaster tools), where you can test and submit sitemaps
6. Boost pages that are close to ranking on page one
 It’s reported that, at a minimum, 75% of clicks go to the first page of search results. If you’re ranking at the top of page two and you’re able to up your positioning to page one, you’re significantly improving your chances of a user selecting your result.
It’s reported that, at a minimum, 75% of clicks go to the first page of search results. If you’re ranking at the top of page two and you’re able to up your positioning to page one, you’re significantly improving your chances of a user selecting your result.
As far as quick SEO wins go, this could take very little time or effort and yield lucrative organic rewards, particularly if you can optimise several pages in this way.
It's easy to fixate on ranking first in the SERPs but if you can get even a handful more of your entries on the first page of Google, you're going to see more traffic and more visitors to your website as a result.
How to give your articles an SEO boost
Understand where your pages are currently ranking for their target keywords. You can do this by tracking the pages in SEMrush (I like to use its Position Tracking feature, which reveals lots of other insightful metrics, too).
"If any pages are ranking in the low teens, do a check to make sure content is optimised appropriately (work back through this article!) and make amendments where necessary."
This step is also where you may need to create new content to boost your authority on the subject. That could be in the form of building pillar pages to create a hub of thematic content, adding related articles to which you can link across, or adding sections to those pages you want to boost to give them that extra authority, weight, and value to the target reader.
Learn more about the specifics of pillar page SEO.
7. Build skyscraper content
 SEO is a slippery beast. Those rankings you've worked so hard to build up can slide on a daily basis. One way of planting your flag in the ground and really showing Google that your article or web page deserves to stay at the top spot is by using the skyscraper technique.
SEO is a slippery beast. Those rankings you've worked so hard to build up can slide on a daily basis. One way of planting your flag in the ground and really showing Google that your article or web page deserves to stay at the top spot is by using the skyscraper technique.
"As well as impressing Google, the skyscraper technique is sure to please your visitors."
Because the technique involves building a page that towers over all other results for that term in the SERPs, any page to which you apply this technique is sure to answer a lot of their questions, help them out, and provide a great deal of value. (Inbound marketing as I live and breathe.)
And you've already read how much Google favours pages that people favour.
The skyscraper technique is also an awesome way of building up backlinks to your site. (But more on backlinks later.) So what actually is this technique and how can you roll it out?
'Skyscraper technique' meaning (and how to build one):
In entrepreneur Ryan Robinson's words, "You start by researching popular trends, topics, and already well-received pieces of existing content across the topic areas your business typically covers."
"Then, you look for new and unique ways to create content that communicates a similar message — with a twist. This might mean that you leverage a new, more engaging medium, update the statistics, or employ a better design." Ryan Robinson
Video is one such way of elevating your content above the competition. According to Search Engine People, 'including a video in a post increases organic traffic from search results by 157%'.
'Once you've created a new and improved piece of content, reach out to the folks that have already linked out to similar content to put your piece on their radar... and hopefully earn a link.'
"If you have a dedicated content writer on your marketing team or in the wider business, this task can be relatively quick and effective when handed across to them."
Drawing from their content marketing expertise, they should be able to create a new page on your site (or optimise an existing page) that 'skyscrapes' the competition and is a magnet for backlinks (and organic traffic).
Better yet, work this technique into your ongoing content strategy and turn skyscraper content into a standard practice for your content team on a weekly or monthly basis.
8. Ensure your pages are formatted properly
 Google certainly favours content that is properly formatted. It (should) go without saying that so do your readers. For both reasons, properly formatting your articles and web pages will help to give your SEO a boost.
Google certainly favours content that is properly formatted. It (should) go without saying that so do your readers. For both reasons, properly formatting your articles and web pages will help to give your SEO a boost.
Well-formatted content typically consists of a H1 tag for your main heading, H2 tags for subheadings, and then H3 tags for any smaller headings. "Don't overlook the basics like writing compelling keyword-rich H1 tags," shares marketing technologist Christopher Perry.
"This is a quick and easy SEO tip because it doesn't take long at all to dive into your website and optimise the pages in this way. Even if your website has lots of pages, prioritising the key ones will help you drive the biggest impact in the fastest possible time.'"
How to successfully format your pages for SEO:
Use your now familiar SEO tools (we're looking at you, SEMrush and ScreamingFrog), make sure each page has only one unique H1 tag.
Go through other content on your site to ensure both the reader and Google can grasp the main topics of your posts through the headings. Are they keyword optimised and do they still make sense?
'Make sure your primary keyword appears in the H1, an H2 or other subheading, and at least once in the body copy', adds Dan.
'Beyond that, best practice is to incorporate a range of related keywords into the content, showing Google that you're a) not spamming your content with your primary keyword and b) writing at breadth using a range of related terms and language.'
9. Review keyword use
 The first step to finding the right keywords to use on your website is to ask the question 'will this keyword be valuable to my visitors?'
The first step to finding the right keywords to use on your website is to ask the question 'will this keyword be valuable to my visitors?'
'Your keywords need to be relevant to your content to keep visitors who are searching for those terms engaged on your website and provide them with value', explains one of our content writers, Aaron Aquilina.
"When researching your keywords, Google them. You might find that the results are dominated by businesses completely different to yours. If this is the case, you may be looking in the wrong area and want to choose a different keyword that may be more relevant." Aaron Aquilina, Copywriter, BabelQuest
Aaron also advises that you consider the intent behind the keyword. 'Is it a commercial term such as "SEO services" or an informative one, say "SEO tips and tricks"? Matching the intent to the page is key to creating content that meets visitor expectations.'
Aaron's best free keyword research tools:
Google Keyword Planner is the best place to begin keyword research. It’s designed for advertising, but you can use it to research organic keywords. Your search can be based on your product or service, your competitor’s landing page and a specific product category.
With Keyword Planner, you can:
- Get ideas for new keyword and ad groups.
- See search volume and other useful metrics for a list of keywords, or group them into ad groups.
- Get traffic forecasts for a list of keywords.
- Use an existing keyword list to get new ideas.
If you plan on doing SEO and paid advertising together, Keyword Planner can help you determine which keywords are better to target organically or with advertising.
Moz’s Keyword Explorer is a great tool that provides some additional dimensions to keyword research. As well as the standard Volume and Keyword Difficulty metrics, Keyword Explorer also offers:
- Opportunity: Relative CTR of the organic results on a SERP
- Importance: How critical the keyword is to your campaign
- Potential: A combination of all keyword metrics
The tool generates its data based on Keyword Planner, Google Suggest, and Related Searches. Moz’s tool is perfect if you already know the keywords you’re targeting but require more insight.
LSIgraph is the best place to go if you already have the main keyword you’re going to be targeting in your content, but you need alternatives to avoid keyword stuffing.
With LSIgraph you get an extremely easy user interface, all you have to do is enter your keyword into the search bar and hey presto, you’re presented with a list of related keywords that have been searched for previously.
How to evaluate keyword statistics (get ahead by knowing your numbers)
The main keyword statistics that you'll need to understand are as followed:
- Volume — The number of times the given keyword is searched for (usually per month but can vary depending on the tool you’re using)
- Keyword difficulty (KD) — An estimate of how difficult it would be to rank organically for the keyword
- Cost per click (CPC) — The average price that users pay for an ad that’s triggered by searching for the keyword
- Competition — How many advertisers are using the given keyword to display their ads
To know how to select the best keyword, analyse the stats. 'Volume isn't always everything; often a mid-length or longer-tail keyword will be easier to rank for and provide much more context, making it simpler to target with page content', says Aaron.
"Did you know that 50% of search queries are four words or longer?"
'We usually suggest targeting a keyword that has a good amount of volume but an easy to medium level of difficulty. This way you’ll be able to rank as highly as possible without having to compete against quite so many websites.'
Related read: Location-Based SEO: How to Rank for a Targeted Area [Beginner's Guide]
10. Optimise your pages for featured snippets
'Make sure your website talks to search engines with clean, structured data; then you can start winning big over larger competitors with rich snippets', adds marketing technologist Christopher Perry.
Featured snippets are the boxes that Google shows between paid-for and organic results. They can take the form of a short paragraph of copy, a list or a table. See one of Christopher's examples from City Catering Southampton below:
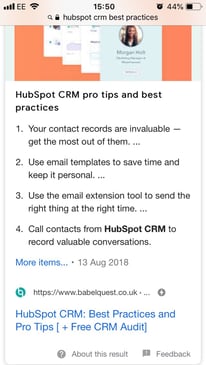
Featured snippets are Google’s nifty way of answering people’s questions without them having to click through to a webpage.
'But wait', I hear you say, 'people don’t click on these things'.
Yes, some people decide they’ve got the answer they need without clicking through to the relevant web page, but many of us do use these boxes to guide us to more detailed advice.
Research by HubSpot reveals that content with a featured snippet gets a 2X higher click-through rate.
One clear reason for this is the fact that featured snippets take up a lot of screen space. In some situations, even the top ranking search result isn’t visible without scrolling.
How do you get your page in featured in a snippet?
So if featured snippets are a great (free) way of sending traffic to your website, how do you get that top spot?
1. Decide which pages to prioritise
Some people call featured snippets ‘answer boxes’. However, Google doesn’t only serve up featured snippets in response to questions.
A study run by SEMrush and Ghergich & Co. analysed 6.9 million snippets. They found that 42% of searches that included questions generated snippets.
This compared to 18% of searches featuring prepositions (e.g. ‘for’ or ‘with’) and 23% of searches featuring comparisons (e.g. ‘vs’ or ‘compare’).
Meanwhile, only 7% of searches without questions, prepositions or comparisons showed a featured snippet.
What does this mean for your ambitions of SEO world domination?
It means that when you’re deciding which pages to optimise for featured snippets, you should focus on the ones designed to answer questions and provide information, rather than those designed to sell or entertain.
2. Tell Google which question you’re answering
Matthew Howells-Barby, from HubSpot, explains how you can do this:
‘There should be an area on the page where the search query appears in a header (H2, H3, H4, etc.). The content you want to appear in the featured snippet (the answer to the query) should be placed in a <p> tag directly below the header mentioned above. This answer should be between 54–58 words long.'
3. Optimise, optimise, optimise
The pages Google features in snippets tend to rank in the top ten. With this in mind, many of the techniques that improve search rankings (and are listed in this article) will help you get closer to bagging that featured snippet spot.
It’s especially important to focus on long-tail keywords. The more words typed into a search box, the greater the chances of a featured snippet appearing.
11. Review your page content
 'Producing content that your prospects actually want to read is the best SEO advice I was given', reveals international marketing manager at Cumulus Networks Paul Sweeney.
'Producing content that your prospects actually want to read is the best SEO advice I was given', reveals international marketing manager at Cumulus Networks Paul Sweeney.
'Too often content is produced for the benefit of Google rather than the humans at the other end of its user face. Produce content people want to read and will find useful, and search engines will reward that.'
Search Engine Land recently reiterated this, with Jessica Bowman — of its editorial team — emphasising 'the importance of training your writing staff to produce high-quality content that is at least as good if not better than your nearest competitors. [My colleague Detlef] Johnson reminded us that Google’s increasingly sophisticated use of machine learning and neural networks is making it possible for the company to understand content on a conceptual level, rather than in terms of matching precise words.'
One thing is clear: content continues to be a driving force behind a page's ability to rank.
For speed, consider any one of the below tips to give your site content a facelift. (Looking longer term? Consider creating a strategy that combines all of the below points for maximum effect.)
How to optimise your website content for search:
What type of content is it?
There are many types of content that people want to read, including articles, case studies, white papers, and guides. Look out for patterns on the first page of Google.
If, for instance, you see that the majority of the results on the first page are guides, it might indicate that the users searching simply want to know more about this topic as their knowledge is basic. This means that you should be writing content to educate people about your product or service because they aren’t ready to purchase anything yet.
How old is the content?
Old content could mean one of two things. Either the content is ‘evergreen’ and is simply just good content that stays valuable no matter how old it is. Or, there’s no new content being produced so the old content, even if it is out of date and poor quality, is still ranking well.
If you find that the content for your keyword is poor and out of date then that’s great news for you. As Search Engine Land recently explained, Google sometimes prioritises new content over old content, so it can be easier to rank highly for certain topics once you've rewritten or refreshed it:
'Many SEOs know [...] that freshness is one of the factors Google considers important, but this doesn’t mean all content calls for frequent updating. Think of the difference between blue whales and protein bars [...] facts about one topic might change much less frequently than facts about the other.'
Does your website feature duplicate content?
If more than one page on your website features the same content, you're sending confusing signals to Google, never mind your site visitors. Every page on your website should have a specific purpose, so if you're finding instances of duplicate content, it could suggest that one or more of your pages are redundant.
If all the pages are necessary and do have a unique purpose, then you should rewrite the content across those pages to make sure it reflects that. The next time Google comes to crawl your site, it will have a much clearer idea of what each page is about — and, crucially, when to return them in the SERPs.
The length of your page content
According to Backlinko, 'the average Google first page result contains 1,890 words'.
Medium research suggests that the average ideal length of a blog post is 1,600 words, which is around seven minutes of reading.
It's easy to assume that no one reads long pages, but I'd urge you to try some out, run a fair test, and see what the data tells you.
Writing longer-form pages gives you more room to explore your subject at greater depth. You'll typically hit way more related keywords, which Google likes. Format it properly (see point 8) to optimise it for digital audiences and turn it into a cornerstone article linking out to lots of your other related posts.
Who is authoring your content?
In the same article cited earlier, Search Engine Land explains how 'Google is getting very good at determining the authority of sources, especially in verticals where authority is particularly important, such as healthcare.'
Attributing the author of your content to the relevant expert, specialist, or authority within your company is one way of improving its credibility — even if only slightly — in the eyes of both your site visitors and Google's bots.
Have you included video content?
It's no secret that video is making waves across the marketing landscape. HubSpot reveals that 'Video content is 50 times more likely to drive organic search results than plain text', lending weight to its use alongside plain-text content to create effective content with significant organic presence.
Related read: 8 Quick and Easy LinkedIn Content Ideas Using Repurposed Content
12. Create a backlink strategy
 You’ve probably come across backlinks before. In case you haven’t, they’re links to your website from other people’s sites.
You’ve probably come across backlinks before. In case you haven’t, they’re links to your website from other people’s sites.
In very simple terms, Google views backlinks as a sign that your site is worth linking to. In the past this has led to some strange things. We’re not talking about alien sightings. We’re talking about website owners spamming strangers, begging for links to their site.
As you might have guessed, this isn't an effective backlink strategy.
For a start, not all backlinks have the same value. Links from trusted, authoritative sources will have the biggest impact on your search rankings. Links from untrusted sources can have a negative impact.
Other things that separate ‘bad’, ‘good’ and ‘better’ backlinks include keywords, nofollow tags and domain relevance.
Three proven backlink strategies
Ultimately, you have to pick the backlink strategy that suits your business. What works for an IT company will not necessarily generate results for a shampoo brand.
If you do nothing else, following step 10 by ensuring that you’re creating content your customers want to read (or watch) is going to serve you well.
This sounds obvious enough, but if your contacts see your pages as valuable they will be more than happy to share them with their contacts.
Here are a three other ways that B2B brands can play to their strengths:
1. Target people who create link roundups
There are plenty of bloggers who do weekly or monthly roundups of the things that are happening in their industry. For example, ‘top ten things happening in retail tech this month’.
Identify who these people are in your industry, then get in touch. Here’s an example of an email used by SEO expert, Brian Dean:
Hi [Site Owner Name],
I just stumbled on your [Saturday Roundup] this afternoon. Good stuff!
I’m just reaching out because I recently published a content marketing case study that might be a good fit: [Your Webpage]
Either way, keep up the awesome work 😀
Cheers,
[Your First Name]
2. Guest blog for influential sites
When I say influential here, I mean those sites where your target persona is likely engaging with content and learning. If you can nestle your articles or videos amongst other authoritative content, you're putting it in a prime position to positively influence their readership — whether that's simply by helping them to understand a concept or process or actively encouraging them to find out more on your site.
Guest blogging can be time consuming initially, but once you've built meaningful relationships with key contacts using a similar outreach email to the example below, it becomes much faster to submit article pitches and see progress.
Hi [Site Owner Name],
I've been reading your blog [Blog name if relevant] for [X] years. I'm a particular fan of your [subject] articles, which have helped me to [briefly explain].
I’m just reaching out because I'm in the process of drafting an article on [subject] that might be a good fit: [Your article title]
If I shared my ideas with you, would you be willing to feature the finished article on your blog?
Either way, keep up the awesome work 😀
Cheers,
[Your First Name]
3. Sign up and contribute to HARO
Perhaps the quickest backlink tactic that springs to mind is HARO (Help a Reporter Out).
Through HARO, reporters or content writers submit questions that they would like industry specialists or other relevant contributors to help them answer.
It's free to sign up and you can receive multiple emails to your inbox every day, each message packed with questions that you or your colleagues may well be able to answer.
"Firing off a quick reply doesn't have to take long and, if accepted, the author may reference you in their article, with a link back to your own website or content."
What I love about HARO is that the authors and writers are essentially coming to you for your contribution. At the same time, you don't have to write much. Simply draw from your expertise or experience to provide valuable insights you know the writer won't be able to resist.
For more tips and tricks, read 'How to Master SEO Trends and Rank Higher on Google'.
Getting to grips with these quick, easy SEO tips and tricks
So much of marketing today requires creativity, time, and patience. In this world, SEO is something you can grab with both hands and work through methodically, safe in the knowledge that you're doing all the right things to optimise your site for organic reach.
And if you still find you need a (third) hand with any of these SEO techniques, know you can always drop a comment below or reach out to us for a chat. Between us, we cover a great swathe of SEO bases. We might just be able to help.
Discover how SEO can help you see a bigger return by downloading our free ebook below.
Heading
Separated they live in Bookmarksgrove right at the coast of the famous Semantics, large language ocean and many more stuff and more more more


Tom is BabelQuest's Principal Copywriter. He has a PhD in Creative Writing from the University of Southampton and is a novelist with Sparkling Books.




.png?width=50)

.png?width=50)
.png?width=50)